Significance of Laboratory Design in Research
Laboratories are the birthplaces of innovation, where groundbreaking discoveries and advancements take shape.
But have you ever considered the significance of the design behind these laboratories?
Laboratory design is not merely about aesthetics; it plays a pivotal role in shaping the course of scientific research. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the profound significance of laboratory design in the world of research, highlighting how a well-thought-out design can foster innovation, efficiency, and safety.
1: Beyond Four Walls
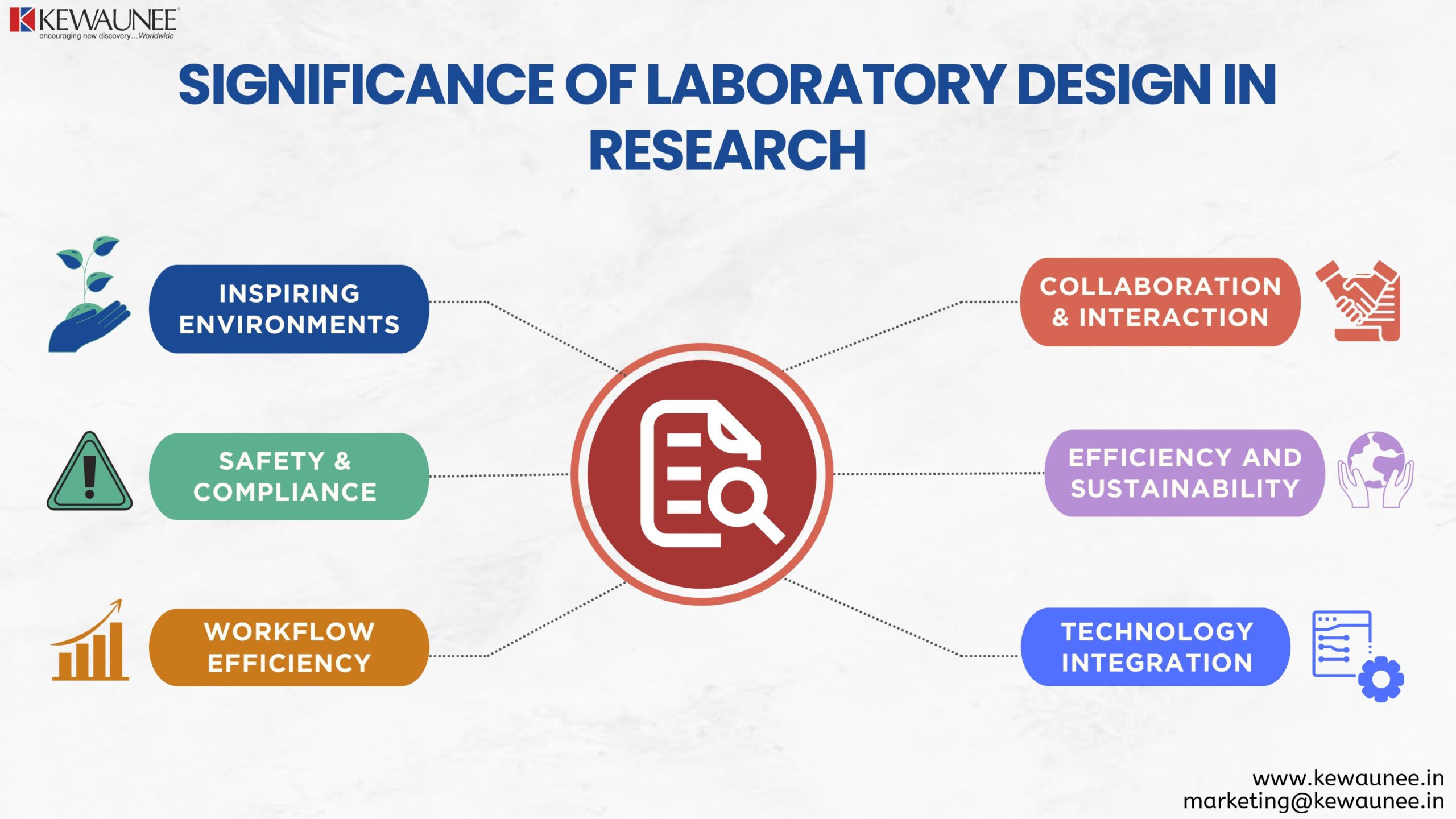
1.1. Creating an Inspiring Environment:
Laboratories should be more than just functional spaces; they should inspire those who work within them. Natural light, ergonomic workstations, and a well-considered layout contribute to a positive atmosphere that encourages creativity and collaboration.
1.2. Flexibility for Evolution:
Scientific research is a dynamic field, and laboratory design should reflect that dynamism. Flexible layouts and adaptable spaces ensure that the laboratory can easily accommodate new equipment, methodologies, and evolving research directions.
2: Safety and Compliance
2.1. Hazard Mitigation:
Safety is paramount in any laboratory setting. An intelligently designed lab integrates safety features like fume hoods, chemical storage, and emergency equipment seamlessly. This minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures strict compliance with safety regulations.
2.2. Containment and Ventilation:
Effective laboratory design includes well-planned ventilation systems, especially for handling hazardous materials. Proper containment and airflow control protect researchers and maintain the integrity of experiments.
3: Workflow Efficiency
3.1. Streamlining Processes:
An intelligently designed lab optimizes workflow. Researchers can move efficiently between workstations, reducing downtime and increasing research productivity.
3.2. Proximity Matters:
Strategic placement of equipment, storage, and support areas is crucial. By locating frequently used equipment closer to workspaces, unnecessary movements are minimized, saving valuable time.
4: Collaboration and Interaction
4.1. Collaboration Spaces:
Modern laboratory design incorporates collaborative areas where researchers can exchange ideas and work together seamlessly. These spaces foster interdisciplinary research and innovation.
4.2. Interaction Zones:
By designing spaces where scientists from different disciplines can interact informally, laboratories encourage the cross-pollination of ideas, often leading to unexpected breakthroughs.
5: Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
5.1. Green Laboratories:
Sustainability is an increasingly important consideration in laboratory design. Green lab design principles aim to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and promote environmentally friendly practices.
5.2. Energy-Efficient Equipment:
Selecting energy-efficient laboratory equipment and systems not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint of research facilities.
6: Technology Integration
6.1. Cutting-Edge Infrastructure:
Incorporating state-of-the-art technology infrastructure into lab design supports advanced research methods, data collection, and analysis, ensuring that researchers have the tools they need to stay at the forefront of their fields.
6.2. Future Proofing:
Anticipating technological advancements ensures that the laboratory remains relevant and adaptable to emerging research techniques. A well-designed lab can accommodate new technologies and methodologies without the need for extensive renovations.
7: Summary
In summary, laboratory design is not a mere afterthought but a cornerstone of scientific research. It goes beyond aesthetics, encompassing safety, functionality, efficiency, and sustainability. A thoughtfully designed laboratory creates an environment where innovation thrives, collaboration flourishes, and research progresses efficiently.
As science continues to evolve, the significance of laboratory design remains undeniably vital—it is the foundation upon which scientific progress is built, and it plays a key role in shaping the future of research and discovery.
Comments are closed.