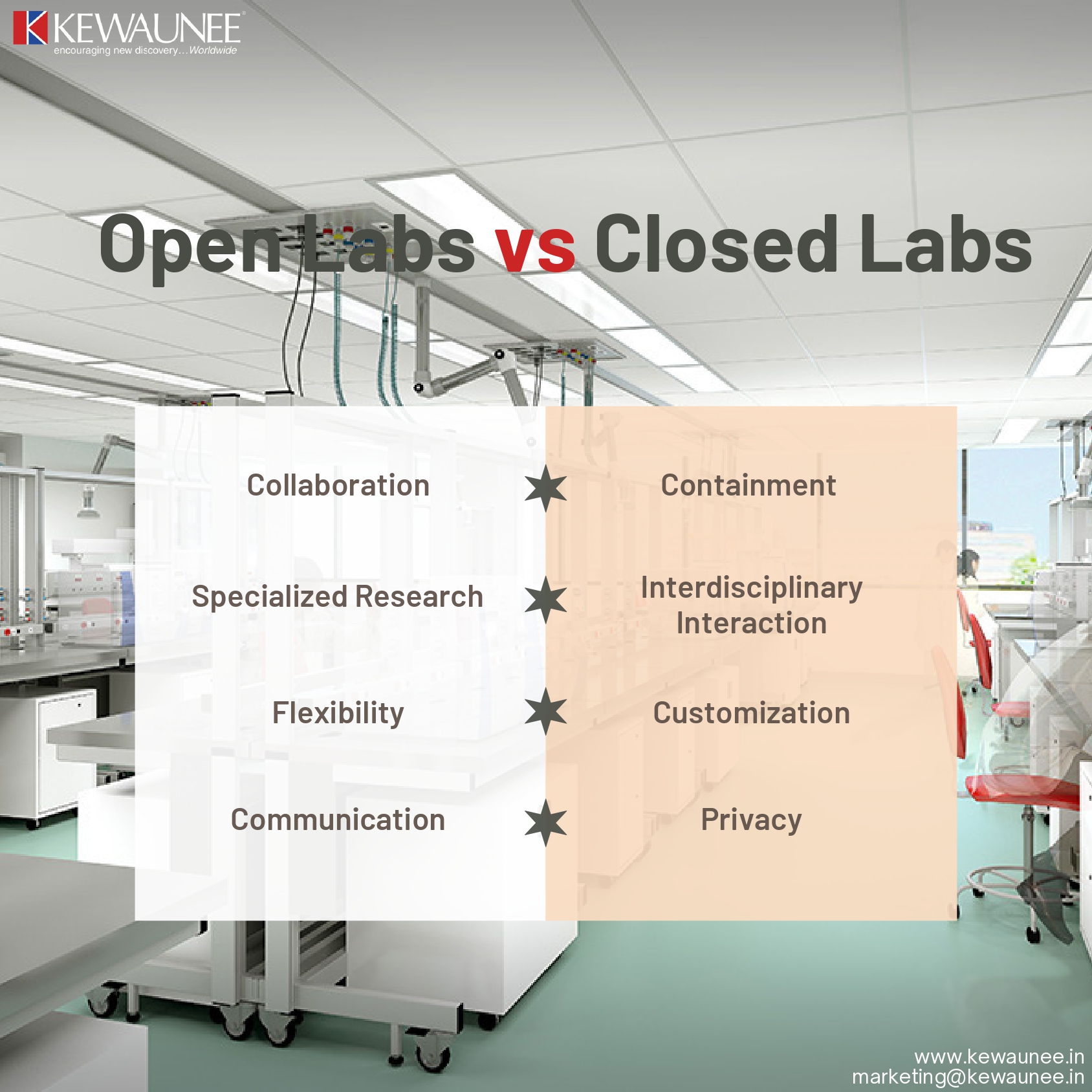
Open vs. Closed: Designing Labs for Collaboration or Containment?
Laboratories are the birthplaces of innovation and scientific discovery. However, the design of these spaces can significantly impact their functionality and the type of research conducted within them.
In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the intriguing debate between open and closed lab designs, exploring the advantages, disadvantages, and considerations of each approach in the context of fostering collaboration or ensuring containment.
1: Open Labs – Fostering Collaboration
1.1. Collaborative Ecosystem:
Open lab designs emphasize open floor plans and shared workspaces, promoting collaboration among researchers. These layouts encourage the free flow of ideas and knowledge.
1.2. Interdisciplinary Interaction:
In open labs, researchers from different disciplines work in proximity, enabling spontaneous interactions and interdisciplinary research. This cross-pollination of ideas often leads to innovative solutions.
2: Closed Labs – Prioritizing Containment
2.1. Containment and Safety:
Closed labs prioritize containment to prevent the release of hazardous materials or pathogens. They feature strict access controls, controlled environments, and safety protocols.
2.2. Specialized Research:
Closed labs are essential for highly specialized research areas like biosafety level (BSL) laboratories, cleanrooms, and chemical containment facilities, where safety is paramount.
3: Design Considerations
3.1. Flexibility:
Open labs are flexible and easily adaptable to changing research needs. Researchers can reconfigure spaces quickly to accommodate new projects.
3.2. Customization:
Closed labs are tailored to specific research requirements, often with fixed infrastructure. Customization ensures the safety and integrity of containment research.
4: Communication and Privacy
4.1. Collaboration in Open Labs:
Open labs encourage communication but may lack privacy. Researchers often use shared spaces for discussions, impromptu meetings, and idea exchange.
4.2. Confidentiality in Closed Labs:
Closed labs provide privacy and confidentiality essential for containment research. Researchers can work with sensitive materials without compromising safety or security.
5: Safety and Regulations
5.1. Compliance in Closed Labs:
Closed labs must adhere to stringent safety regulations and standards, such as those governing biosafety, chemical storage, and cleanroom operation.
5.2. Safety Protocols in Open Labs:
Open labs prioritize safety but may require more vigilance to maintain safety standards and prevent cross-contamination.
6: Finding the Balance
6.1. Hybrid Approaches:
Some laboratories combine open and closed spaces to balance collaboration and containment needs. This approach allows for flexibility while ensuring safety.
6.2. Research Goals:
The choice between open and closed lab designs should align with the specific research goals and priorities of the institution or project.
Summary
In summary, the debate between open and closed lab designs is a complex one, rooted in the objectives of the research being conducted. Open labs foster collaboration and interdisciplinary interaction, ideal for innovative and collaborative research. In contrast, closed labs prioritize containment and safety, making them indispensable for specialized research requiring strict safety protocols.
Ultimately, the choice between open and closed lab designs depends on the research goals and the nature of the work. Some laboratories find success in hybrid approaches that strike a balance between collaboration and containment. The key is to design laboratory spaces that best serve the needs of the researchers and the safety of the community, ensuring that innovation and safety can coexist harmoniously in the world of scientific discovery.
Comments are closed.