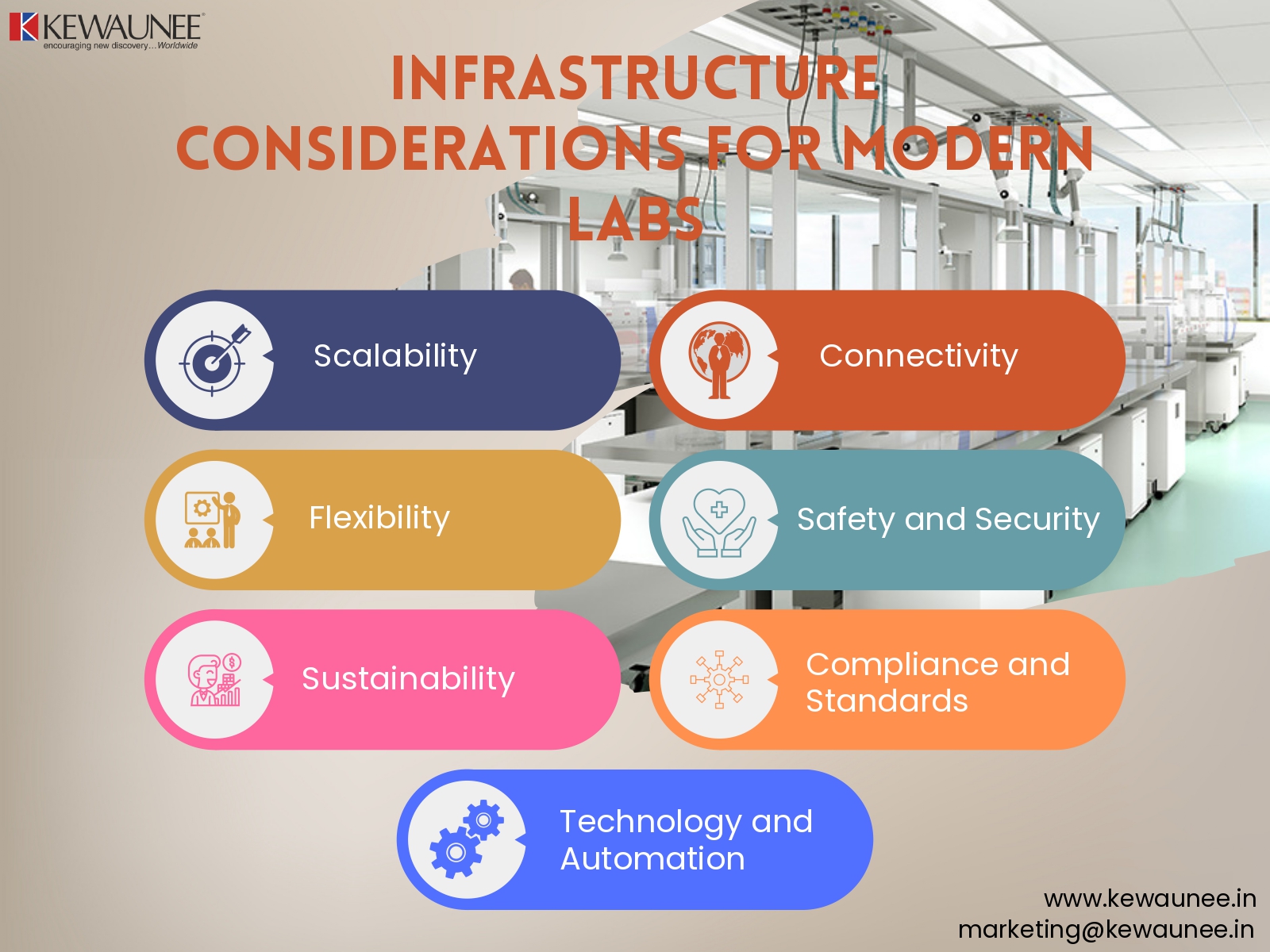
Infrastructure Considerations for Modern Labs
Modern infrastructure plays a critical role in enhancing the efficiency, productivity, and safety of laboratory operations. With advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of scientific research, laboratories need to have robust infrastructure to support their evolving needs.
The design and implementation of modern lab infrastructure can significantly impact the quality of scientific outcomes, the well-being of laboratory personnel, and the overall success of research and development endeavors.
When it comes to modern lab infrastructure, there are three key considerations that laboratories should prioritize: connectivity, flexibility, and scalability.
- Connectivity ensures that laboratories have reliable high-speed internet and network connectivity, allowing for seamless data transfer, collaboration, and access to online resources. It enables researchers to stay connected with colleagues, access shared data and resources, and leverage cloud-based solutions for storage and analysis.
- Flexibility in lab infrastructure involves designing adaptable workspaces that can accommodate changing research needs and evolving technologies. This includes modular lab designs that allow for easy reconfiguration, flexible furniture and equipment arrangements, and spaces that foster multi-disciplinary collaboration.
- Scalability is crucial to ensure that lab infrastructure can support growth and expansion. It involves having infrastructure that can accommodate additional equipment, personnel, and research projects without major disruptions. Scalable IT infrastructure, such as cloud-based solutions, allows laboratories to easily scale up or down their computing resources based on demand.
Connectivity in Modern Lab Infrastructure
A. High-speed internet and network connectivity requirements
In today’s digital age, laboratories heavily rely on fast and reliable internet connections to support their research activities. High-speed internet is essential for seamless communication, accessing online resources, collaborating with remote colleagues, and utilizing cloud-based tools and platforms.
Laboratories should ensure that their infrastructure provides sufficient bandwidth to handle data-intensive tasks and support the growing need for real-time collaboration and data transfer.
B. Data integration and interoperability
Modern laboratories generate vast amounts of data from various sources, including instruments, experiments, and simulations. To derive meaningful insights and facilitate efficient data analysis, it is crucial to have robust data integration and interoperability capabilities in the infrastructure.
This involves implementing standardized data formats, seamless integration between instruments and data management systems, and interoperability with other laboratory software and platforms.
C. Wireless and mobile connectivity for enhanced mobility
In addition to wired connectivity, modern lab infrastructure should provide wireless and mobile connectivity options. Wireless networks enable researchers to move freely within the lab while staying connected to data, resources, and colleagues.
Mobile connectivity allows scientists to access lab-related information, monitor experiments, and even control instruments remotely using smartphones or tablets. These capabilities enhance flexibility, productivity, and collaboration within the laboratory environment.
Flexibility in Modern Lab Infrastructure
A. Modular lab design for adaptable workspaces
Flexibility in lab infrastructure starts with the design of the physical space. Modular lab designs offer the flexibility to reconfigure the workspace as research needs evolve. This can involve using movable walls, modular furniture, and flexible bench arrangements that can be easily adjusted to accommodate different research projects or teams. Modular designs also facilitate efficient space utilization and future expansion without major renovations.
B. Flexible furniture and equipment arrangements
Apart from the overall lab design, the selection of furniture and equipment also plays a crucial role in creating a flexible workspace. Adjustable benches, ergonomic chairs, and mobile storage solutions enable researchers to customize their workstations according to their specific needs. Flexible equipment arrangements, such as mobile carts or modular shelving systems, allow for easy reconfiguration and adaptability to different experimental setups.
C. Designing for multi-disciplinary collaboration
Modern research often involves interdisciplinary collaboration, requiring labs to provide spaces that facilitate teamwork and knowledge sharing. Designing collaboration areas, such as meeting rooms, breakout spaces, or shared workstations, encourages scientists from different disciplines to interact, exchange ideas, and work together on projects. These collaborative spaces should be equipped with appropriate connectivity, audiovisual tools, and whiteboards to foster effective communication and brainstorming sessions.
Scalability in Modern Lab Infrastructure
A. Infrastructure that accommodates growth and expansion
Scalability is a critical consideration in modern lab infrastructure design. Laboratories should plan their infrastructure to accommodate future growth and expansion without major disruptions or costly renovations. This includes ensuring adequate space for additional equipment, storage, and personnel. Scalable infrastructure should also consider the capacity for increased power and utility requirements as research activities intensify.
B. Scalable IT infrastructure and cloud-based solutions
Information technology (IT) infrastructure is a crucial component of lab scalability. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability in terms of storage, computing power, and software resources. Labs can leverage cloud services to scale up or down their computational resources based on the demand of their research projects. Additionally, cloud-based storage allows for flexible and secure data management, enabling seamless collaboration and data sharing among researchers.
C. Planning for future technology advancements
Lab infrastructure should be designed to accommodate future technology advancements. This involves staying updated with emerging technologies and understanding their potential impact on laboratory operations. Considering the infrastructure requirements for technologies like automation, robotics, or advanced analytical instruments allows labs to future-proof their infrastructure and avoid costly retrofitting or disruptions to ongoing research activities.
Laboratory Safety and Security
A. Designing for safety and compliance
Safety is a paramount concern in laboratory environments. Modern lab infrastructure should be designed with safety in mind, incorporating safety features and adhering to relevant safety regulations and guidelines. This includes proper ventilation systems, safety cabinets for hazardous materials, emergency shower and eyewash stations, and fire suppression systems. Designing for safety also involves minimizing risks associated with chemical, biological, and radiation hazards through appropriate storage and handling protocols.
B. Access control and restricted areas
Lab infrastructure should include access control measures to ensure restricted areas are only accessible to authorized personnel. This can be achieved through the use of keycard systems, biometric authentication, or other access control mechanisms. Restricted areas may include hazardous material storage areas, equipment rooms, or spaces with sensitive or classified research.
C. Data security and privacy considerations
With the increasing reliance on digital data and electronic records, protecting data security and privacy is crucial. Modern lab infrastructure should include measures to safeguard sensitive research data from unauthorized access, data breaches, or cyber threats. This involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures, regular data backups, encryption protocols, and secure access controls for data management systems.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
A. Green building practices for energy conservation
Modern lab infrastructure should embrace energy-efficient practices to minimize environmental impact and reduce operating costs. This can include incorporating energy-efficient building materials, efficient insulation, and advanced windows for better temperature control. Designing the lab layout to optimize natural lighting and utilizing energy-efficient lighting solutions, such as LED fixtures, can significantly reduce energy consumption.
B. Efficient HVAC systems and lighting solutions
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable and safe lab environment. Modern lab infrastructure should utilize HVAC systems that are energy-efficient and designed to provide adequate air quality, temperature control, and humidity regulation. Similarly, implementing efficient lighting solutions, such as motion sensors and automatic shut-off, can further reduce energy waste.
C. Recycling and waste management strategies
Sustainability should be integrated into lab infrastructure by implementing proper recycling and waste management strategies. Labs generate various types of waste, including chemical waste, biological waste, and electronic waste. Implementing recycling programs, proper waste segregation, and safe disposal practices are essential to minimize environmental impact and comply with relevant regulations.
Equipment and Instrumentation Considerations
A. Adequate space and utilities requirements
Modern lab infrastructure should account for the space and utility requirements of equipment and instrumentation. Each type of equipment may have specific spatial, electrical, or plumbing needs that must be considered during the lab design phase. Proper spacing between equipment, access to utilities, and ergonomic considerations for instrument operation should be incorporated to ensure efficiency, safety, and ease of use.
B. Ergonomic considerations for user comfort and productivity
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in ensuring the well-being and productivity of lab personnel. Modern lab infrastructure should consider ergonomic principles when designing workstations, seating arrangements, and instrument placement. Ergonomically designed furniture, adjustable work surfaces, and proper lighting can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries and promote a comfortable working environment.
C. Future-proofing for emerging technologies
The field of scientific research is constantly evolving, and new technologies and instruments continue to emerge. Modern lab infrastructure should account for the potential adoption of emerging technologies, ensuring that the space, power, and connectivity requirements can accommodate these advancements. Future-proofing lab infrastructure saves time and resources by avoiding the need for extensive renovations or reconfigurations when incorporating new instruments or technologies.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
A. Understanding relevant regulations and standards
Modern lab infrastructure must comply with various regulations and standards depending on the nature of research conducted. This may include compliance with health and safety regulations, environmental regulations, ethical guidelines, and quality management standards. Understanding the specific regulatory requirements and incorporating them into the lab design process ensures compliance and promotes a safe and ethical research environment.
B. Compliance with health, safety, and environmental guidelines
Laboratories must adhere to strict health, safety, and environmental guidelines to protect the well-being of personnel and minimize environmental impact. Modern lab infrastructure should incorporate design features and practices that align with these guidelines. This includes implementing proper ventilation systems, containment measures for hazardous materials, waste management protocols, and safety training programs for personnel.
C. Quality management systems and certifications
Quality management systems, such as ISO 9001 or Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), are essential in maintaining consistent and reliable research outcomes. Modern lab infrastructure should support the implementation of quality management systems, including processes for documentation, traceability, calibration, and equipment maintenance. Laboratories may also pursue relevant certifications to demonstrate their commitment to quality and compliance.
Budgeting and Project Planning
A. Assessing project requirements and budget allocation
Before embarking on lab infrastructure projects, it is crucial to assess the specific requirements and allocate a budget accordingly. This involves understanding the research goals, the scope of the project, the size of the lab, and the expected lifespan of the infrastructure. A thorough assessment allows for accurate budgeting and resource allocation, ensuring that the lab infrastructure meets the intended objectives.
B. Collaboration with architects, engineers, and contractors
Lab infrastructure projects require collaboration between various professionals, including architects, engineers, and contractors. Collaborating with experienced individuals or firms specialized in lab design and construction ensures that the infrastructure is built to meet the specific needs of the research activities. Regular communication and coordination among all stakeholders throughout the project are crucial for its success.
C. Project management and timeline considerations
Effective project management is essential for the timely completion of lab infrastructure projects. Establishing clear project timelines, milestones, and deliverables helps to track progress and ensure that the project stays on schedule. Regular project monitoring, risk assessment, and proactive problem-solving minimize delays and ensure that the lab infrastructure is ready to support research activities within the expected timeframe.
The Role of Technology and Automation
A. Integration of laboratory information management systems (LIMS)
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) streamline data management, sample tracking, and workflow automation. Modern lab infrastructure should integrate LIMS to enhance data integrity, traceability, and collaboration. LIMS enable researchers to efficiently manage data, track samples, and generate reports, ultimately improving productivity and ensuring regulatory compliance.
B. Automation and robotics for increased efficiency
Automation and robotics play a crucial role in modern lab infrastructure, especially for repetitive or time-consuming tasks. Automated liquid handling systems, robotic sample preparation, and high-throughput screening platforms can significantly increase efficiency, reduce human errors, and accelerate research workflows. Incorporating automation-friendly infrastructure, such as robotic workstations or integrated robotic arms, optimizes the use of automation technologies.
C. Data analytics and AI-driven insights
Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have revolutionized scientific research. Modern lab infrastructure should support the integration of data analytics tools and AI-driven insights to extract meaningful information from vast datasets. Implementing infrastructure that allows seamless data integration, storage, and processing empowers researchers to gain valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and accelerate scientific discoveries.
Future Trends in Lab Infrastructure
A. Internet of Things (IoT) applications in the lab
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to revolutionize lab infrastructure by connecting instruments, devices, and data systems. IoT applications in the lab enable real-time monitoring of experiments, remote access to instruments, and predictive maintenance. Modern lab infrastructure should consider IoT integration to enhance operational efficiency, data collection, and decision-making processes.
B. Virtual and augmented reality for remote collaboration
Virtual and augmented reality technologies offer new possibilities for remote collaboration and training in lab settings. These technologies enable researchers to virtually explore lab environments, manipulate virtual objects, and collaborate with colleagues from different locations. Modern lab infrastructure should embrace virtual and augmented reality capabilities to enhance remote collaboration, training programs, and knowledge sharing.
C. Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring systems
Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring systems leverage sensor technologies and data analytics to detect equipment failures, anticipate maintenance needs, and optimize lab operations. Modern lab infrastructure should incorporate these systems to minimize downtime, increase equipment lifespan, and improve overall lab efficiency. Real-time monitoring also enables proactive response to critical events, ensuring the safety of personnel and research continuity.
Conclusion
Modern lab infrastructure is crucial for supporting scientific advancements, fostering collaboration, and ensuring the safety and efficiency of laboratory operations. By prioritizing connectivity, flexibility, scalability, and other key considerations, labs can create an environment that facilitates innovation, productivity, and successful research outcomes.
Connectivity, flexibility, and scalability are fundamental aspects of modern lab infrastructure. Robust connectivity enables seamless collaboration, data transfer, and access to online resources. Flexibility allows labs to adapt to evolving research needs and promote multidisciplinary collaboration. Scalability ensures that lab infrastructure can accommodate growth, new technologies, and expanding research capabilities.
Designing modern lab infrastructure requires a holistic approach that considers not only the physical layout but also the integration of technology, safety measures, sustainability, and compliance with regulations. By creating a supportive and efficient research environment, labs can inspire innovation, foster collaboration, and contribute to scientific advancements across various disciplines.
In summary, modern lab infrastructure plays a crucial role in facilitating scientific research and discovery. By prioritizing connectivity, flexibility, scalability, safety, sustainability, and integration of technology, labs can create an environment that promotes collaboration, efficiency, and innovation. As research needs continue to evolve, lab infrastructure must adapt to support emerging technologies and ensure the success of scientific endeavors.
Comments are closed.