Cleanroom Design in Ensuring Product Quality
In industries where product purity and precision are paramount, cleanrooms play a crucial role. These controlled environments are meticulously designed to maintain exceptionally low levels of particulate contamination, temperature, humidity, and other critical factors.
Cleanroom design is not merely an architectural endeavor; it’s a science that ensures product quality, safety, and compliance with stringent regulations. In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted significance of cleanroom design in various industries.
1. Understanding Cleanrooms
Cleanrooms are specialized environments with a controlled level of contamination that is crucial for research, manufacturing, or other processes. These controlled environments find applications in industries where even minor contaminants can compromise product quality or pose safety risks.
Some of the key features of cleanrooms include:
- Particulate Control: Cleanrooms are designed to control the concentration of airborne particles, including dust, microbes, and chemical vapors.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Cleanrooms often maintain precise temperature and humidity levels to ensure consistent conditions for processes and products.
- Airflow Control: Air circulation is carefully managed to prevent the introduction of contaminants and to remove airborne particles efficiently.
2. Industries That Rely on Cleanrooms
Cleanrooms are utilized across a range of industries where product quality and safety are paramount. Some of the primary sectors that heavily rely on cleanroom environments include:
a) Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
In the pharmaceutical and biotech industries, cleanrooms are indispensable. They are used for drug manufacturing, bioprocessing, and research. Contamination control is critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of medications and biopharmaceuticals.
b) Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics and semiconductor industries require cleanrooms for the production of microchips, integrated circuits, and other sensitive electronic components. Even microscopic contaminants can disrupt the functionality of these devices.
c) Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use cleanrooms for surgeries, research laboratories, and the production of sterile medical devices. Maintaining a sterile environment is essential to prevent infections and ensure patient safety.
d) Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, cleanrooms are used for assembling and testing spacecraft, satellites, and sensitive instruments. Any contamination could compromise the functionality of these mission-critical systems.
3. Cleanroom Design Principles
Effective cleanroom design is a multidisciplinary endeavor that incorporates principles from architecture, engineering, and microbiology. Key factors that influence cleanroom design include:
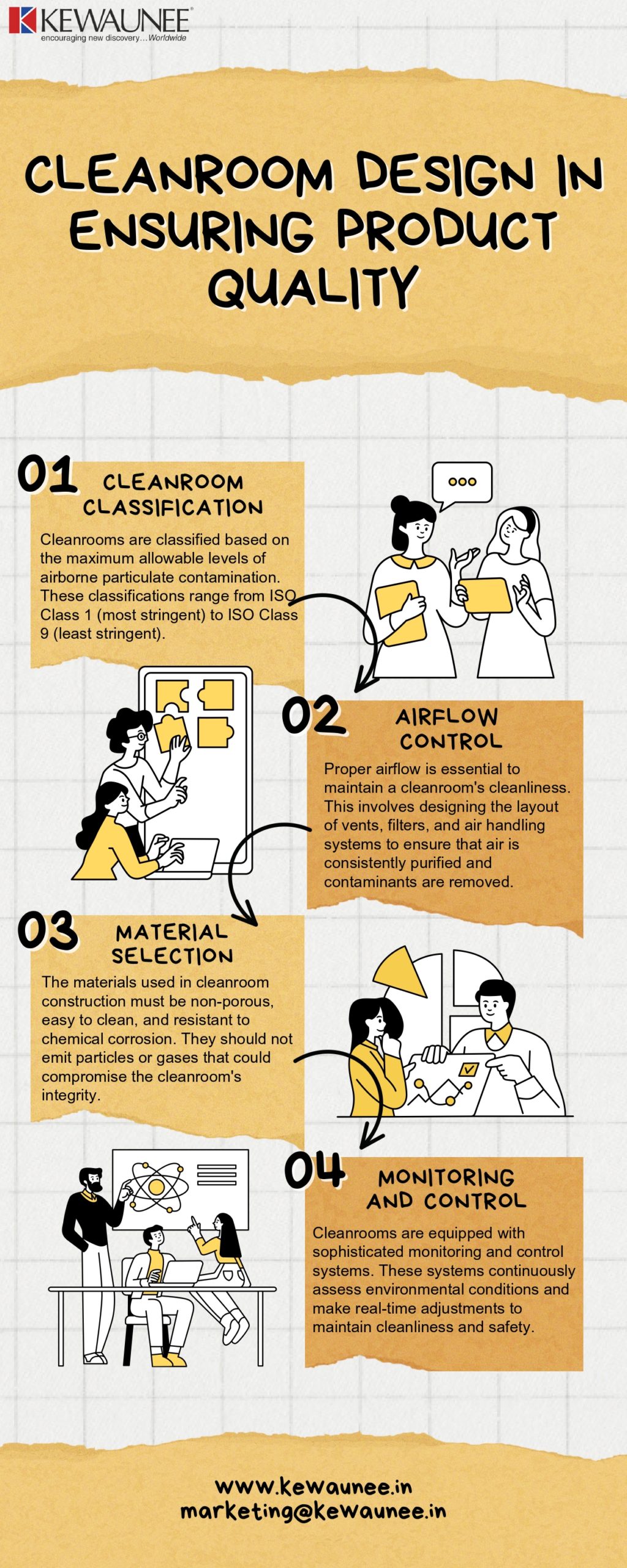
a) Cleanroom Classification
Cleanrooms are classified based on the maximum allowable levels of airborne particulate contamination. These classifications range from ISO Class 1 (most stringent) to ISO Class 9 (least stringent). The choice of classification depends on the specific industry and application.
b) Airflow Control
Proper airflow is essential to maintain a cleanroom’s cleanliness. This involves designing the layout of vents, filters, and air handling systems to ensure that air is consistently purified and contaminants are removed.
c) Material Selection
The materials used in cleanroom construction must be non-porous, easy to clean, and resistant to chemical corrosion. They should not emit particles or gases that could compromise the cleanroom’s integrity.
d) Monitoring and Control
Cleanrooms are equipped with sophisticated monitoring and control systems. These systems continuously assess environmental conditions and make real-time adjustments to maintain cleanliness and safety.
4. Cleanroom Compliance and Regulations
Cleanrooms must adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards. Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the pharmaceutical industry or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide guidelines for cleanroom design and operation. Compliance ensures that products meet safety and quality standards.
5. Ensuring Product Quality
Cleanroom design’s ultimate goal is to ensure product quality. By maintaining a controlled environment, cleanrooms minimize the risk of product contamination and defects. This is especially critical in industries where product reliability is non-negotiable.
Summary
Cleanroom design is an intricate discipline that plays a pivotal role in various industries. Its impact extends beyond architecture and engineering; it directly influences product quality, safety, and compliance with regulations.
In pharmaceuticals, electronics, healthcare, and aerospace, cleanrooms are the guardians of product integrity, ensuring that the final output meets the highest standards of purity and reliability. Cleanroom design exemplifies the fusion of science and engineering in the service of product quality and safety.
Comments are closed.