Industry 4.0 and Manufacturing: Smarter and Efficient Facilities
The fourth industrial revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0, has ushered in a new era of manufacturing. At the heart of this revolution is the Internet of Things (IoT), a technology that connects physical objects and systems to the digital world. In this blog, we’ll explore how Industry 4.0 and IoT are transforming manufacturing, making facilities smarter and more efficient.
1. Introduction
Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing. It’s all about interconnectedness, data-driven decision-making, and automation. At its core, IoT plays a pivotal role by providing a network that links machines, sensors, and processes, creating a seamless flow of information.
The transition to Industry 4.0 is driven by the need for greater efficiency, sustainability, and responsiveness in manufacturing. In this digital age, manufacturers are harnessing the power of IoT to meet these demands. Let’s delve deeper into the impact of IoT in various aspects of manufacturing.
2. The Role of IoT in Manufacturing
2.1. Connecting Machines and Devices
IoT enables the connection of machinery and devices on the factory floor. These smart devices can communicate with each other, share data, and make real-time decisions. For instance, sensors on production machines can relay information on operating conditions, allowing other machines to adjust their processes accordingly. This interconnectivity results in more agile and adaptive manufacturing systems.
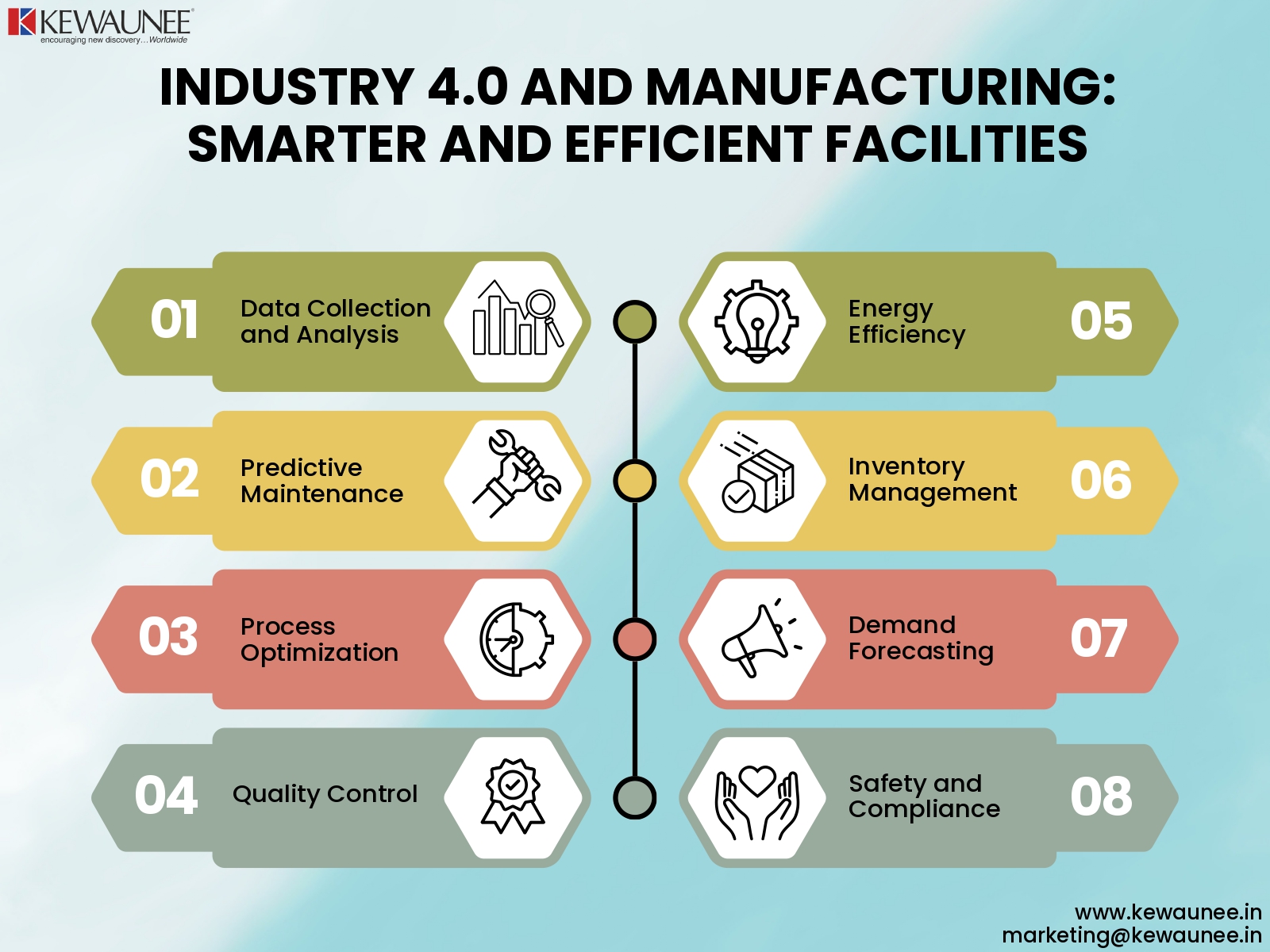
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices is a goldmine for manufacturers. Data is collected and analyzed to gain insights into processes, performance, and potential improvements. For example, sensors in a production line can monitor temperature, humidity, and pressure, providing data that can be used to optimize the production environment. This data-driven approach leads to better decision-making and increased operational efficiency.
2.3. Predictive Maintenance
One of the significant benefits of IoT is predictive maintenance. Sensors on equipment can detect wear and tear, allowing for proactive maintenance to prevent breakdowns. Traditional maintenance routines are often based on time-based schedules, leading to unnecessary maintenance and potential equipment failures. With IoT, maintenance becomes predictive, reducing downtime and saving on repair costs.
3. Smart Manufacturing Processes
3.1. Process Optimization
IoT-driven data analysis can lead to process optimization. Manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, making operations more streamlined. For instance, real-time monitoring of machine performance allows for immediate adjustments when deviations from optimal performance occur. This results in more efficient production processes and cost savings.
3.2. Quality Control
Real-time data collection and analysis enable better quality control. Manufacturers can detect defects or deviations from standards immediately, reducing waste and improving product quality. Sensors and cameras can be employed to inspect products during the production process, ensuring that only products meeting the highest standards reach the market.
3.3. Energy Efficiency
IoT also plays a role in energy management. Manufacturers can monitor energy consumption in real time and make adjustments for more efficient energy use. For example, lighting, heating, and cooling systems can be controlled based on real-time occupancy and environmental data, reducing energy wastage.
4. Supply Chain Integration
IoT extends its reach beyond the factory floor. It connects with suppliers, logistics, and distribution centers, creating a transparent and efficient supply chain.
4.1. Inventory Management
Real-time tracking of inventory levels ensures that manufacturers have the right materials at the right time, reducing storage costs and delays. IoT allows for a dynamic supply chain where inventory levels are adjusted in response to real-time demand, preventing stockouts and overstock situations.
4.2. Demand Forecasting
IoT and data analytics can help predict demand more accurately, allowing for better inventory planning and cost savings. By analyzing historical data and market trends, manufacturers can adjust their production schedules and inventory levels to meet changing customer demand more effectively.
5. IoT-Enabled Automation
Automation is a key component of Industry 4.0, and IoT is the enabler. Machines and robots can be controlled and monitored remotely, increasing efficiency and reducing the need for manual intervention. Automation, guided by real-time data and analytics, allows manufacturers to achieve higher levels of precision and consistency in their production processes.
6. Safety and Compliance
IoT enhances safety in manufacturing. Sensors can monitor environmental conditions and alert workers to potential hazards. Additionally, data can be used to ensure that facilities comply with regulatory standards. For example, air quality sensors can detect the presence of harmful gases, ensuring the safety of workers. Additionally, data records can be used to demonstrate compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
7. Challenges and Concerns
While Industry 4.0 and IoT offer immense benefits, there are challenges and concerns. These include data security, the need for a skilled workforce, and the initial investment required for IoT implementation.
7.1. Data Security
The interconnected nature of IoT introduces new security risks. Manufacturers must ensure that their IoT networks are protected from cyber threats. Data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are essential to safeguard sensitive information.
7.2. Skilled Workforce
Implementing and maintaining IoT systems require a skilled workforce. Manufacturers must invest in training and development to ensure that employees can operate and troubleshoot IoT technologies effectively. Skilled workers are critical for the success of IoT implementations.
7.3. Initial Investment
The initial cost of implementing IoT technologies can be substantial. Manufacturers need to budget for the acquisition of sensors, communication infrastructure, and data analytics tools. While the upfront investment is significant, the long-term benefits in terms of cost savings and operational efficiency justify the expenditure.
Summary
Industry 4.0 and IoT have the potential to revolutionize manufacturing. The integration of IoT technologies creates smarter, more efficient facilities that optimize processes, improve quality, and reduce costs. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, embracing these innovations is essential for staying competitive and meeting the demands of a rapidly changing market.
In conclusion, the future of manufacturing is undeniably intertwined with Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, we can expect even greater transformations in the manufacturing landscape. Embracing IoT is not just a choice; it’s a necessity for manufacturers looking to thrive in the digital age. The benefits in terms of efficiency, quality, and competitiveness are too significant to ignore. Industry 4.0 and IoT are here to stay, and those who embrace them will lead the way in the future of manufacturing.
Comments are closed.