Laboratory Exhaust Treatment Systems Demystified
Laboratories are hotbeds of scientific exploration, but they also generate a range of potentially harmful emissions and pollutants. To protect both the environment and laboratory personnel, specialized laboratory exhaust treatment systems are employed.
In this comprehensive blog, we will unravel the intricacies of these systems, exploring their design, components, and the vital role they play in ensuring safe and responsible laboratory operations.
1: The Need for Laboratory Exhaust Treatment
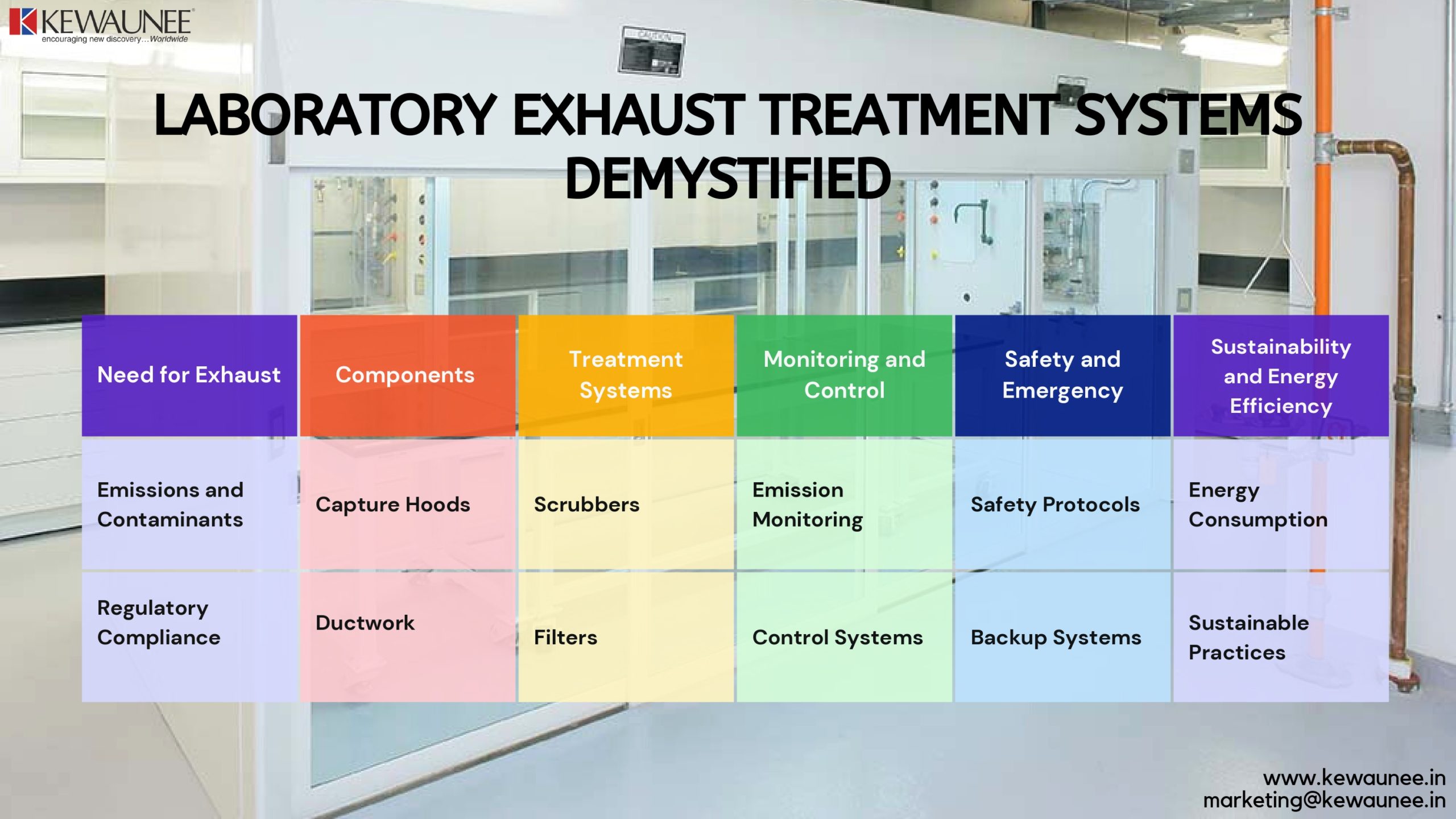
1.1. Emissions and Contaminants:
Laboratories produce a variety of emissions, including chemical fumes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. Some of these emissions can be hazardous to human health and the environment.
1.2. Regulatory Compliance:
Stringent environmental regulations require laboratories to control and treat their emissions to meet air quality standards and protect the surrounding community.
2: Components of Laboratory Exhaust Treatment Systems
2.1. Capture Hoods:
Capture hoods are placed at the source of emissions to collect pollutants effectively. They play a critical role in capturing contaminants before they disperse into the atmosphere.
2.2. Ductwork:
Ductwork connects the capture hoods to the treatment system. Proper design and maintenance are essential to ensure efficient pollutant transport.
3: Treatment Systems
3.1. Scrubbers:
Scrubbers use a liquid or gas to absorb, neutralize, or remove pollutants from the exhaust air. Different types of scrubbers are used based on the nature of the emissions.
3.2. Filters:
Filters, such as activated carbon or HEPA filters, can be employed to capture and remove specific pollutants or particulate matter from the exhaust air.
4: Monitoring and Control
4.1. Emission Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring of emissions ensures that treatment systems are functioning correctly and that pollutant levels are within acceptable limits.
4.2. Control Systems:
Sophisticated control systems regulate the operation of exhaust treatment systems, optimizing their efficiency and performance.
5: Safety and Emergency Measures
5.1. Safety Protocols:
Laboratories must have safety protocols in place to respond to system failures or emergency situations, preventing the release of hazardous materials.
5.2. Backup Systems:
Redundant systems or backup power sources can provide an additional layer of protection in case of system failure.
6: Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
6.1. Energy Consumption:
Efforts are made to design and operate exhaust treatment systems efficiently, minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
6.2. Sustainable Practices:
Some laboratories explore sustainable practices, such as energy recovery from exhaust air, to reduce their carbon footprint.
Summary
In summary, laboratory exhaust treatment systems are essential components of responsible laboratory operations. They help control and treat emissions, protecting the environment and ensuring compliance with stringent regulations. The components of these systems, including capture hoods, ductwork, scrubbers, and filters, work together to capture and neutralize pollutants.
Continuous monitoring and control systems provide oversight, while safety measures and sustainability efforts enhance the overall performance and environmental responsibility of laboratory operations. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is crucial for laboratories committed to responsible research and environmental stewardship.
Comments are closed.